When you are in trouble - Disasters
Typhoons
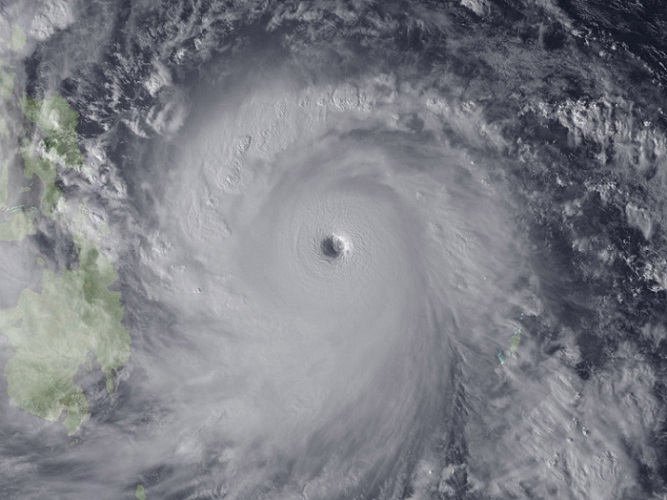
You can get information about typhoons in Japan from Japan Meteorological Agency. Beside, when typhoons are near to Japan, Japanese media report its strength and pathes. Unfortunately, when you encounter typhoons while traveling Japan, please stay indoor and abstain from going outside in only one day because normally, typhoons move up north at 10-20 kilometers per hour and move other areas from place where you are in a day. Beside, please keep mind that you should not approach coasts because of high tides.
Rainy Season
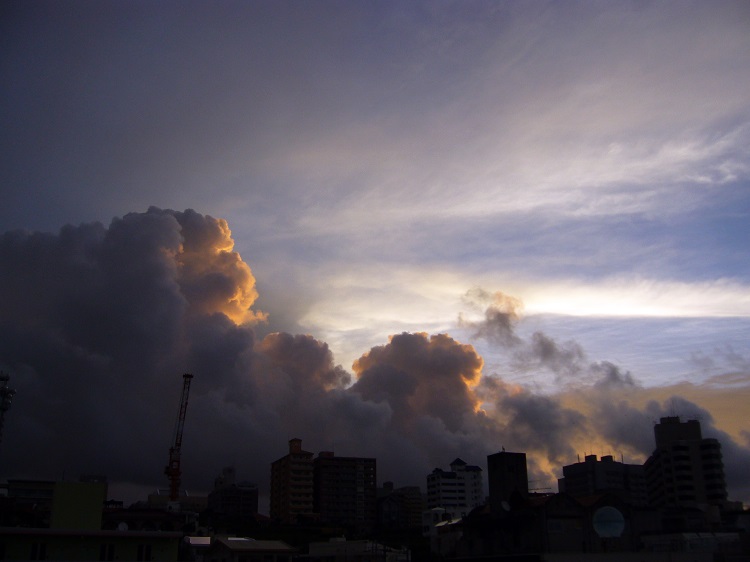

In Japan, it rains often between June and July, and the rainy season is called "Tsuyu (梅雨)". Moreover, summer in Japan is very humid, so the weather is unsettled. Therefore, localized torrential rain happens many times in Tuyu season. In Japan, the localized torrential rain is called "Guerrilla rain (ゲリラ豪雨)" because it hits in a short time like a guerrilla attack, and it is not rare that it rain more than 100 mm per hour. Such heavy rain is caused by cumulonimbus - abnormal huge cloud. If you see such cloud, unbelievable heavy rain will attack area where you are as soon as you see even if it is pleasant weather.
Earthquakes
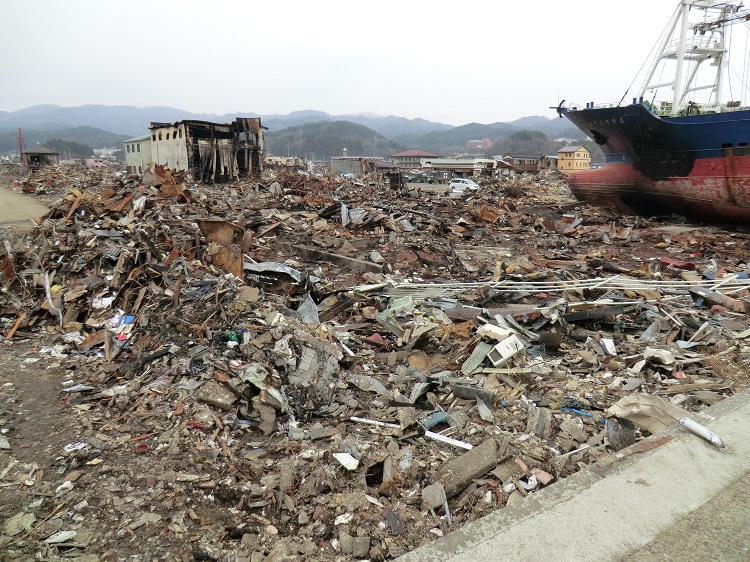

This photo is taken by xtcbz
Japan is located on some continental and oceanic plates, so earthquakes and tsunamis, big waves caused by earthquakes, occur easily in Japan. The number of all earthquake that occur in Japan every year including both large and small is more than 1,000, so it can be said that there are few days that earthquakes do't occur in Japan. However, most of them are small earthquakes. Earthquakes are evaluated according to 10 seismic intensity (Shindo, 震度), the levels showing how large earthquakes are, in Japan, and more than 99 % of earthquakes occuring in Japan are categorized into 1st-3rd seismic intensity. In other word, almost all earthquakes don't damage anything.Seismic Intensity Scale |
People's Reactions |
Indoor Situation |
Outdoor Situation |
Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 Seismic Intensity |
People cannot feel a quake. | - |
- |
0.0-0.6 |
1st Seismic Intensity |
Only a few people who are silent inside feel a quake slightly. | - |
- |
0.7-2.0 |
2nd Seismic Intensity |
Many people who are silent inside feel a quake Some sleeping people wake up. | Hung things such as lumps are swing slightly. | - |
2.1-3.4 |
3rd Seismic Intensity |
Almost all people inside and some walking people feel a quake. Many sleeping people wake up. | Things in shelves shake and hit each other. | Electric wire swing slightly. | 3.5-4.3 |
4th Seismic Intensity |
Almost all people are surprised at vibration. Almost all walking people feel a quake, and almost all sleeping people wake up. | Hung things such as lumps are swing considerably and things in shelves rattle. Some unstable things fall. | Electric wire swing. Some people riding a bicycle feel a quake. | 4.4-4.9 |
Lower 5th Seismic Intensity |
Many people are frightened and want to hold on to fixed things. | Hung things such as lumps are swing violently, and some things in shelves fall. Many unstable things fall, and some unfixed furniture moveor fall. | Occasionally, window panes are broken, and its piece fall. Utility poles swng, and some unreinforced roads are damaged. | 5.0-5.5 |
Upper 5th Seismic Intensity |
Many people cannot walk without holding on to fixed things. A quake obstructs people's actions. | Many things in shelves fall. Many unfixed furniture fall or fall. | Sometimes, window panes are broken, and its piece fall. Some unreinforced concrete-block walls and vending machines fall. It is to hard to drive a car, and some cars are stopped. | 5.6-6.1 |
Lower 6th Seismic Intensity |
It is hard for people to stand even if they hold on to fixed things. | Almostall unfixed furniture move or fall. Some door frames are warped, and some door canot open. | Some tiles on walls and windows panes are broken and its piece fall. | 6.2-6.7 |
Upper 6th Seismic Intensity |
People cannot stand, and crawling is only a way of moving for people. Some people are thrown by a quake. | Almost all unfixed furniture fall. | Many tiles on walls and windows panes are broken and its piece fall. Almost all unreinforced concrete-block walls collapse. | 6.8-7.3 |
7th Seismic Intensity |
Almost all unfixed furniture fall. Some of them jump up. | Almost all tiles on walls and windows panes are broken and its piece fall. Some reinforced concrete-block walls collapse. | 7.4- |
When you are indoor,
- Do not rush outside.
- Leave from windows, large furniture, and unfixed thing.
- Get under the table, and protect you head.
- Leave from buildings, block walls, and windows.
- Be careful of falling things.
- Protect your head by bags or clothes from broken glass.
- Do not rush to the exit.
- Follow the attendant's instructions.
- Do not rush to the exit.
- Hold on to fixed things, and peovide against emergency stop.
After the quake stop, you must ensure your safety. If you are near to sea or river, leave from sea or river and go to eminences quickly. Tsunami (big waves caused by earthquakes) may hit after eartuquake. Also, you need to be careful of fire. Turn off the gass, stoves, and heaters. Leaking gasoline or gas can easily catch fire from sparks of cut electric cables, so leave from vehicles even if it stopped. If your radio or TV work, please turn it on and get information about the earthquake.
After the earthquake strike, aftershocks may occur. Therefore, without relaxing, wait for rescue.
Example of Earthquake Early Warnings: